
Close

what can go wrong?
Who might be harmed and how ?
Evaluate the risks (how bad? how often?)
Record your ufb01ndings (Risk Register)
Propose action and identify who is responsible and target date.
Review your assessment and update if necessary.
Understand what is likely to go wrong and how and why it may go wrong.
Take into account things that have gone wrong in the past and near-miss incidents.


Patient, staff, or others; consider the number of patients or staff that might be affected over a stated period of time.
Remember that the most vulnerable patients are more likely to suffer harm.
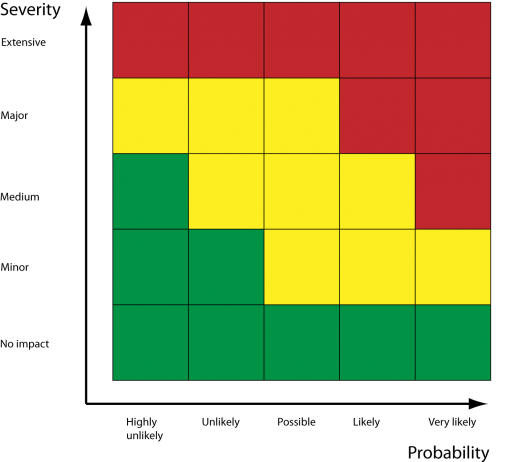
How bad? How often? is there a need for further action?
Consider consequence (how bad?- severity) and likelihood (how often?- probability). Use risk matrix
Is there a need for additional action?.
The assessment findings is recorded. An efficient and succinct system of documentation is essential.
Good documentation is important because things are always changing, and those changes can alter existing and/or introduce new hazards.
The solutions to reduce the risk to acceptable level, who is responsible and target date.
It may be reasonable to accept some degree of preventable risk, if the benefits to be gained outweigh the risk.


Review your assessment and update :