Telemedicine refers to the delivery of healthcare services through digital communication technologies, such as video conferencing, phone calls, messaging, and…
Hospital Assessment Tool Version 3
Patient Safety Assessment Manual (PSAM) PSAM contains a set of standards with requirements that are needed for the establishment of…
Improving Patient Flow
Improving patient flow is an important aspect of healthcare delivery as it can reduce wait times, increase patient satisfaction, and…
Patient Flow
Patient flow refers to the movement of patients through the healthcare system, from the point of initial entry to the…
An Accountable or A Second Victim
In 1994, when I was an anesthesia intern, a bride and groom were admitted to the operating theater after a…
A.I. and PCI – Machines Vs Human
A new machine-learning analysis revealed that an algorithm can offer a decision on the appropriateness of coronary revascularization during pressure-wire pullback at…
Ten Facts on Patient Safety
FACT 01 Patient harm is the 14th leading cause of the global disease burden, comparable to diseases such as tuberculosis…
Improving Geriatric Healthcare
A program for geriatric healthcare should focus on promoting the health and well-being of elderly individuals and should include the following
Geriatric Healthcare
A program for geriatric healthcare should focus on promoting the health and well-being of elderly individuals and should include the following
Patient Safety Assessment Manual
This manual provides the necessary tools for professional associations, regulatory, accrediting or oversight bodies and ministries of health, to improve…
Pt. Safety Friendly Hospitals
A study conducted in 2009 in six countries of the Eastern Mediterranean Region showed that up to 18% of hospital admissions were…
Janet Brown in her own wards
On July 23, 1995, my life changed dramatically. I sustained a spinal cord injury and incomplete quadriplegic in a car…
Patient Safety Officer
The Patient Safety Officer (PSO) has the primary responsibility to coordinate and serve as a resource for the development, implementation,…
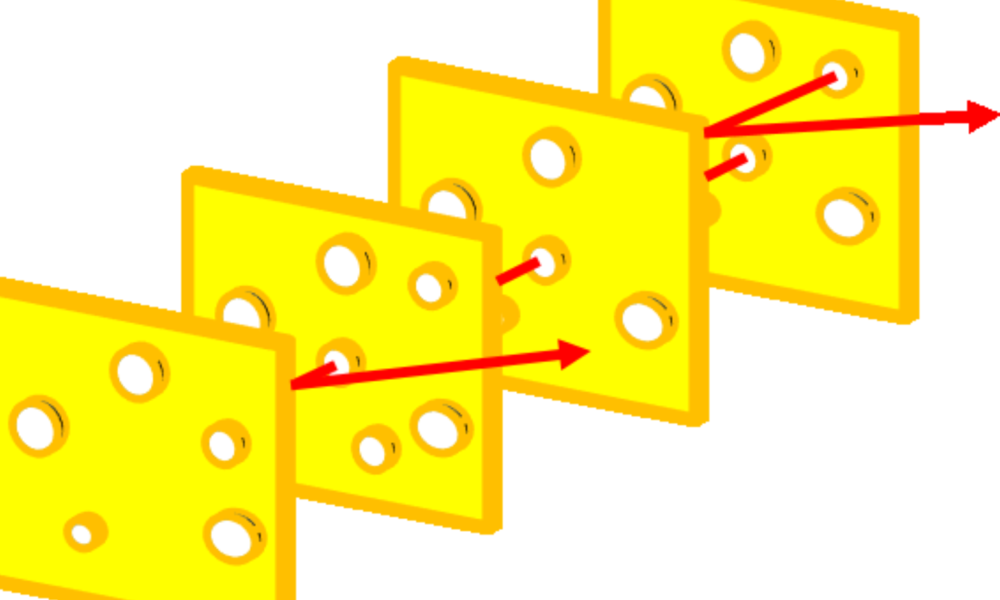
Swiss Cheese Model
The Swiss Cheese Model is a widely used framework for understanding and analyzing how errors can occur in complex systems,…
Leadership and Patient Safety
Leadership is considered the main factor for an effective patient safety program. The Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) developed a…
Patient Safety Principles
Systems design Patient safety starts with system design. The safe system consists of procedures, the environment, the design of the…
Pt. Safety Story – Bill Aydt
As told by Bill’s daughter, Karen Curtiss. Dad was lucky, at first. He was in the final stages of a…
Pt. Safety Stories – Alicia Cole
Alicia Cole had been a successful working actress whose only experience with healthcare was playing doctors on TV. All that…
The Three Behaviors
ABC model of attitudes Affective component This involves a person’s feelings / emotions about the attitude object. For example: “I…
HAMs Harmful Errors
Identification of High Alert Medications (HAMs) differs from one institution to another. However, all organizations identify four specific HAM drug…
Quality and Patient Safety
Patient safety is about how healthcare organizations protect their patients from errors. While many hospitals are good at keeping their patients…
Medication Reconciliation
A shared patient safety problem worldwide is the lack of accurate and complete information about patients’ medicines when their care…
High Alert Medications
While any medication potentially can cause harm, a select group of drugs—high-alert medications (HAMs)—carries a higher risk of patient injury.…
Patient Identification
The success of many treatments and activities within healthcare facilities depends on ensuring that correct patient identity has been established. Patient…